©2025 Cognivue, Inc. | Privacy Policy | References
The Dementia Literacy Assessment (DeLA): A novel measure of Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders health literacy in diverse populations46
Authors: James E. Galvin, Deborah M. Germain, Claudia P. Moore, Jennifer A. Jeanty, Vaatausili Tofaeono, Lisa K. Wiese
Journal: Alzheimer’s & Dementia
Year Published: 2025
Key Findings: DeLA increased dementia health literacy and performed well across different participant characteristics (age, sex, education, geographic locale, race, ethnicity, and cognitive performance). Gains in ADRD health literacy were associated with older age, more education, better socioeconomic status, greater resilience, and better cognitive performance. Cognivue Clarity was used as an additional cognitive validator in this study.
Gait, balance, and physical performance as markers of early Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia risk42
Authors: Magdalena I. Tolea, Amie Rosenfeld, Sam Van Roy, Lilah M Besser, Deirdre M. O’Shea, James E. Galvin
Journal: Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease
Year Published: 2025
Key Findings: 1) changes in mini PPT performance and balance may help detect cognitive impairments, as early as the SCD stage; 2) changes in gait speed, gait cycle parameters, and Timed Up-and-Go may indicate more significant cognitive impairment; 3) neuronal loss is linked to subtle changes in physical functionality as early as SCD. Physical performance may be a valuable tool in early dementia detection in clinical settings and could identify targets for early intervention. Cognivue Clarity was used as an additional cognitive validator in this study.
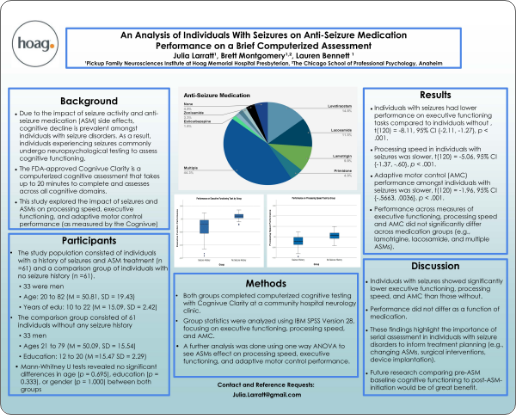
An Analysis of Individuals With Seizures on Anti-Seizure Medication Performance on a Brief Computerized Assessment45
Authors: J Julia Larratt, Brett Montgomery, Lauren Bennett
Conference Poster: International Neuropsychological Society (INS)
Year Presented: 2025
Key Findings: Cognivue Clarity® was used as part of a study exploring the impact of seizure activity and anti-seizure medication (ASM) on processing speed, executive functioning, and adaptive motor control performance. Findings showed that individuals with seizures showed significantly lower executive functioning, processing speed, and adaptive motor control than those without.
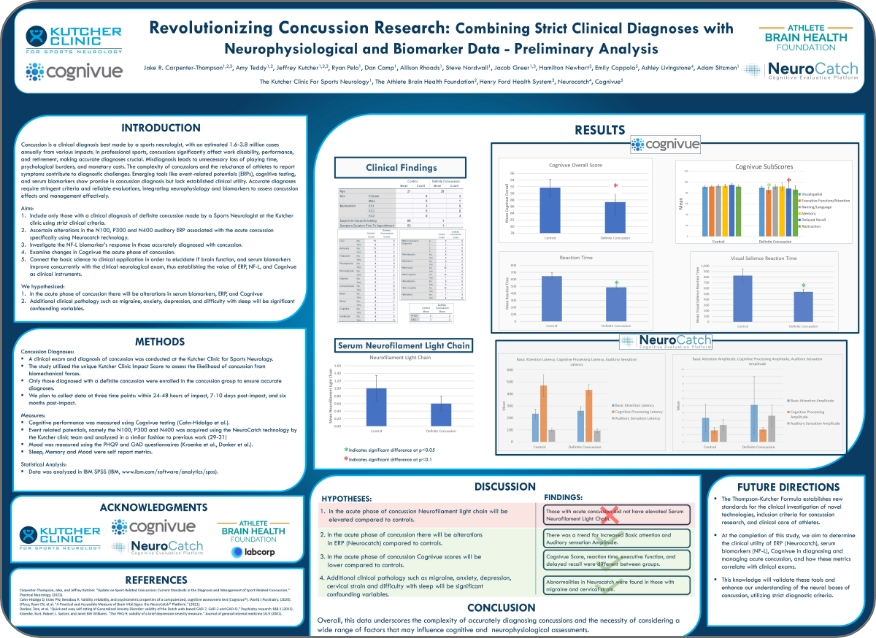
Revolutionizing Concussion Research: Combining Strict Clinical Diagnoses with Neurophysiological and Biomarker Data – Preliminary Analysis43
Authors: Jake R. Carpenter-Thompson, Amy Teddy, Jeffrey Kutcher, Ryan Pelo, Dan Camp, Allison Rhoads, Steve Nordwall, Jacob Greer, Hamilton Newhart, Emily Coppola, Ashley Livingstone, Adam Sitzman
Conference Poster: Big Sky Sports Medicine Conference
Year Presented: 2025
Key Findings: Cognitive performance was measured using Cognivue Clarity and found significant differences in scores between those in the acute phase of concussion and the control group. Assessment of all the poster data underscores the complexity of accurately diagnosing concussions and the necessity of considering a wide range of factors that may influence cognitive and neurophysiological assessments.
Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2024 report of the Lancet standing Commission37
Authors: Gill Livingston, Jonathan Huntley, Kathy Y. Liu, Sergi G. Costagreda, Geir Selbæk, Suvarna Alladi, et alt
Journal: The Lancet
Year Published: 2024
Key Findings: Update since the 2020 report of the Lancet Commission on dementia added two new modifiable risk factors for dementia (vision loss and high LDL cholesterol) to the 12 previously identified risk factors (less education, hearing loss, traumatic brain injury, hypertension, alcohol, obesity, smoking, depression, social isolation, physical inactivity, air pollution, and diabetes). The commission also calculated that around 45% of dementia cases are potentially preventable by addressing these 14 modifiable risk factors.
APOE ε4 carrier status moderates the effect of lifestyle factors on cognitive reserve38
Authors: Deirdre M. O’Shea, Andrea S. Zhang, Katana Rader, Rebecca L. Shakour, Lilah Besser, James E. Galvin
Journal: Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease
Year Published: 2024
Key Findings: Significant interactions were found between APOE ε4 status and mindfulness and social engagement on cognitive reserve, indicating stronger associations for APOE ε4 carriers. Cognivue Clarity was used in the estimation of cognitive reserve in this study.
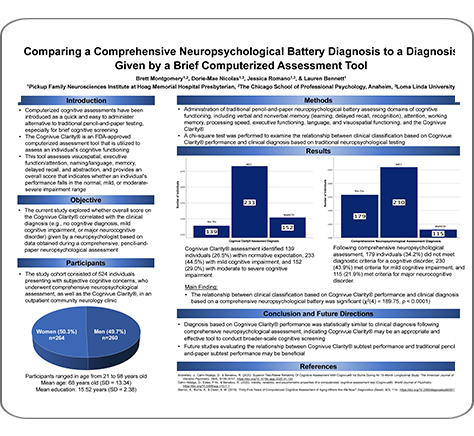
Comparing a Comprehensive Neuropsychological Battery Diagnosis to a Diagnosis Given by a Brief Computerized Assessment Tool32
Authors: Brett Montgomery, Dorie-Mae Nicolas, Jessica Romano, Lauren Bennett
Conference Poster: The International Neuropsychological Society Meeting (INS)
Year Presented: 2024
Key Findings: Diagnosis based on Cognivue Clarity® performance was statistically similar to clinical diagnosis following comprehensive neuropsychological assessment, indicating Cognivue Clarity® may be an appropriate and effective tool to conduct broader-scale cognitive screening.
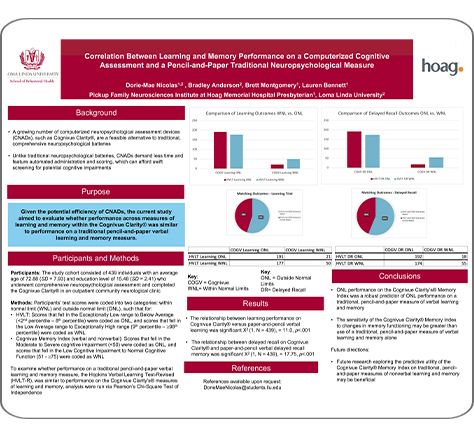
Correlation Between Learning and Memory Performance on a Computerized Cognitive Assessment and a Pencil-and-Paper Traditional Neuropsychological Measure33
Authors: Dorie-Mae Nicolas, Bradley Anderson, Brett Montgomery, Lauren Bennett
Conference Poster: The International Neuropsychological Society Meeting (INS)
Year Presented: 2024
Key Findings: ONL performance on the Cognivue Clarity’s® Memory Index was a robust predictor of ONL performance on a traditional, pencil-and-paper measure of verbal learning and memory. The sensitivity of the Cognivue Clarity® Memory Index to changes in memory functioning may be greater than use of a traditional, pencil-and-paper measure of verbal learning and memory alone
Use of a Computerized Assessment Tool in Individuals with a History of Seizures44
Authors: Brett Montgomery, Megan Maguire, Christopher Reeves, Jessica Romano, Julia Larratt, Lauren Bennett
Conference Poster: The American Epilepsy Society (AES)
Year Presented: 2024
Key Findings: Findings suggest that Cognivue Clarity® may be a suitable tool for screening assessments in individuals with a history of seizures. Considering the reliance on serial monitoring and integrating multiple clinical tools in managing this population, Cognivue Clarity offers a potentially efficient, effective, and expedient option for enhancing comprehensive patient care.
Hearing intervention versus health education control to reduce cognitive decline in older adults with hearing loss in the USA (ACHIEVE): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial28
Authors: Frank R. Lin, James R. Pike, Marilyn S. Albert, Michelle Arnold, Sheila Burgard, et al.
Journal: The Lancet
Year Published: 2023
Key Findings: Over 3 years, in older adults at increased risk for cognitive decline, hearing intervention slowed down loss of thinking and memory abilities by 48%.
Cognitive screenings in otolaryngology? The time has come17
Authors: Douglas L Beck, Jedidiah J Grisel
Journal: Journal of Otolaryngology-ENT Research
Year Published: 2022
Key Findings: Article reviews the current knowledge related to cognition and audition and explores the practical reasons for incorporating cognitive screening into otolaryngology clinics, with specific regard to patients with hearing and listening problems.
The emerging relationship between cognition and audition: why cognitive screenings are beneficial for audiology patients and why comprehensive audiometric evaluations are recommended for people with mild cognitive impairment, cognitive decline or dementia.18
Authors: Douglas L Beck
Year Published: 2022
Key Findings: This report explores the emerging relationship between cognition and audition and why it is important to suspect, test, document and manage these relationships as early as possible. There often exists an opportunity to alter the trajectory of cognitive decline, if early intervention is facilitated.
Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission1
Authors: Gill Livingston, Jonathan Huntley, Andrew Sommerland, David Ames, Clive Ballard, etc al
Journal: The Lancet
Year Published: 2020
Key Findings: Confirmed data from 2018 report and added three new modifiable risk factors (excessive alcohol consumption, head injury, and air pollution). Modifying 12 risk factors might prevent or delay up to 40% of dementias: less education, hearing loss, traumatic brain injury, hypertension, alcohol, obesity, smoking, depression, social Isolation, physical inactivity, air pollution, and diabetes. Be ambitious about prevention.
Hearing loss and cognition: a discussion for audiologists and hearing healthcare professionals19
Authors: Douglas L Beck, Sarah Bant, Nathan A Clarke
Journal: Journal of Otolaryngology-ENT Research
Year Published: 2020
Key Findings: Article discusses evidence concerning hearing loss and cognition and how it relates to people living with hearing loss and cognitive decline or dementia.
Psychotropic Polypharmacy in Adults 55 years or Older: A Risk for Impaired Global Cognition, Executive Function, and Mobility21
Authors: Gilles Loggia, Elpidio Attoh-Mensah, Kristell Pothier, Remy Morello, Pascale Lescure, et al
Journal: Frontiers in Pharmacology
Year Published: 2020
Key Findings: The threshold of two daily psychotropic molecules increases the risk of impaired executive function, global cognition, and mobility, independent of cofounding factors, including comorbidities.
Risk reduction of cognitive decline and dementia: WHO guidelines14
Authors: World Health Organization
Year Published: 2019
Key Findings: These guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations on lifestyle behaviors and interventions to delay or prevent cognitive decline and dementia.
Associations between polypharmacy and cognitive and physical capability: a British birth cohort study20
Authors: Mark James Rawle, Rachel Cooper, Diana Kuh, Marcus Richards
Journal: J Am Geriatr Soc
Year Published: 2018
Key Findings: Polypharmacy at age 60 to 64 and 69 was associated with poorer physical and cognitive capability, even after adjusting for disease burden. Stronger negative associations were seen in participants with longstanding polypharmacy, suggesting a cumulative, dose-dependent relationship.
Association of Polypharmacy with 1-Year Trajectories of Cognitive and Physical Function in Nursing Home Residents: Results from a multicenter European Study22
Authors: Davide Liborio Vetrano, Emanuele Rocco Villani, Giulia Grande, Silvia Giovannini, Maria Camilla Cipriani, et al
Journal: Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine
Year Published: 2018
Key Findings: Polypharmacy is associated with worsening cognitive function over 1 year.
Dementia prevention, intervention, and care13
Authors: Gill Livingston, Andrew Sommerlad, Vasiliki Orgeta, Sergi G Costafreda, Jonathan Huntley, et al
Journal: The Lancet
Year Published: 2017
Key Findings: The number of people with dementia is increasing globally. Be ambitious about prevention. Modifying 9 risk factors might prevent or delay up to 35% of dementias: less education, hearing loss, hypertension, obesity, smoking, depression, physical inactivity, social isolation, and diabetes.
A review of new insights on the association between hearing loss and cognitive decline in ageing16
Authors: S. Fortunato, F. Forli, V. Guglielmi, E. De Corso, G. Paludetti, et al
Journal: Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica
Year Published: 2016
Key Findings: These guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations on lifestyle behaviors and interventions to delay or prevent cognitive decline and dementia.
Polypharmacy Cut-Off for Gait and Cognitive Impairments23
Authors: Antoine Langeard, Kristell Pothier, Remy Morello, Veronique Lelong-Boulouard, Pascale Lescure
Journal: Frontiers in Pharmacology
Year Published: 2016
Key Findings: Community-dwelling adults ages 55 years and older who take five or more daily medications are at a high risk for both mobility and cognitive impairments.
Hearing Loss and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults15
Authors: Frank R. Lin, Kristine Yaffe, Jin Xia, et al
Journal: JAMA Internal Medicine
Year Published: 2013
Key Findings: Hearing loss is independently associated with accelerated cognitive decline and incident cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older adults.